Abaca

Abaca, also known as Manila Hemp, is a natural fibre originating from the Philippines. Derived from the banana family, it boasts sturdy plant stems, making it a resilient and hard fibre with a wide range of applications.
Key Uses:
Abaca finds its application in various industries, including:
- Rugs
- Bags
- Hats
- Canvas
- Ropes
- Hammocks

Advantages
- Durable
- Strength
- Flexibility
- Resistance to Salt Water Damage
Disadvantages
- Shrinks in Water
Acetate

Acetate, originating in the early 20th century, is a synthetic fibre that stands among the initial manufactured fibres. Formulated by utilising cellulose derived from wood pulp or cotton linters, acetate has garnered widespread acclaim, particularly for its distinctive features and versatile applications.
Key Uses:
Acetate finds its application in various industries, including:
- Drapery
- Lingerie
- Hats
- Outerwear
- Mittens
- Scarves

Advantages
- Hydrophilic
- Soft
- Little Shrinkage
- No Static
- Breathable
Disadvantages
- Dry Clean or Hand Wash Only
- Poor Abrasion Resistance
- Poor Heat Retention
Acrylic

Acrylic, a revolutionary synthetic fibre that emerged in the 1940s, has since become a staple in the textile industry. Crafted from shorter staples akin to wool and transformed into yarn, it stands as an exceptional alternative to Cashmere, offering a comparable luxurious feel. This versatile fibre can be tailored to imitate the textures of both wool and cotton, catering to diverse preferences.
Key Uses:
Acrylic finds its application in various industries, including:
- Upholstery
- Tracksuits
- Hats
- Faux Fur
- Carpets
- Sweaters

Advantages
- Thermal Retentive
- Stronger than Wool
- Machine Washable
- Hydrophobic
- Resilient
Disadvantages
- Carries Static
- Low Absorbency
- Heat Sensitive
Agneline

Agneline, a distinctive black woolen fabric, captures attention with its very long nape, offering a coarse and heavy texture. This fabric stands out due to its intriguing properties that contribute to its specific uses and distinctive qualities.
Key Uses:
Agneline finds its application in various areas, with notable uses including:
- Trims
- Collars
- Evening Coats

Advantages
- Water-Resistant
- Resilient
Disadvantages
- Coarse
- Heavy
Albert Cloth

Albert Cloth, named in honour of Prince Albert, stands as a distinguished fabric crafted from wool. This double-sided textile, often adorned with patterns on each face, radiates regality and is primarily tailored for outerwear, notably double-breasted overcoats. Its rich history and association with royal nomenclature add a touch of sophistication to this exceptional fabric.
Key Uses:
Agneline finds its application in various areas, with notable uses including:
- Outerwear
- Overcoats

Advantages
- Durability
- Elegance & Sophistication
- Double-Sided Design
Disadvantages
- Limited Versatility
- Specialised Care
- Weight
Bamboo

With advanced treatments, bamboo fabric has become more versatile. It was originally used in corsets and is now used for a variety of purposes. The fiber is made from bamboo cellulose and has a variety of uses.
Key Uses:
Bamboo finds its application in various industries, including:
- T-Shirts
- Casual Clothing
- Bags

Advantages
- Good Dimensional
- Stability
- Non-Static
- Durable
- Hydrophillic
Disadvantages
- Poor elasticity
- Not resistant to mildew
Banana Silk

This fiber is created by combing banana stalks together to create yarn. A satin-like appearance, despite being coarse, makes it a finer alternative to bamboo.
Key Uses:
Banana silk finds its application in various industries, including:
- Tablecloths
- Curtains
- Upholstery
- Bags
- Floor Matts
- Authentic Kimonos

Advantages
- Durable
- Smooth
- Satin-Like Appearance
- Biodegradable
Disadvantages
- Course
- Rare
Barathea

Typically made from wool, silk, or cotton, Barathea is a twill fabric that is woven in a hopsack pattern. Evening coats, jackets, and military uniforms are often made from it, which provides a slight pebbled finish.
Key Uses:
Barathea finds its application in various industries, including:
- Military Uniform
- Neckties
- Evening Coats
- Jackets

Advantages
- Price
- Machine Washable
Disadvantages
- High Maintenance
- Limited Versatility
Batik

Batik is a traditional fabric characterized by its unique dyeing process, which uses wax-resist techniques to create intricate patterns and designs. Originating in Indonesia, batik is an art form that involves applying wax to the fabric in specific areas, dyeing the fabric, and then removing the wax to reveal the pattern. This process can be repeated multiple times with different colors to create layered and complex designs. Batik fabrics are used in a variety of cultural and contemporary clothing, as well as in home decor, showcasing vibrant colors and distinctive motifs.
Key Uses:
Batik fabrics finds its application in various industries, including:
- Dresses, Skirts & Shirts
- Scarves
- Home decor

Advantages
- Durable
- Versatile
Disadvantages
- Stiff
- High Maintenance
Explore Our Batik Fabrics
-
Premium Quality 100% Cotton Batik - 45" Wide (Brown)
£595£1800Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar -
Premium Quality 100% Cotton Batik - 45" Wide (Yellow & Navy)
£595£1099Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar -
Premium Quality 100% Cotton Batik - 45" Wide (Sun Set)
£595£1099Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar
Batiste

The Cambric fabric, known for its plain weave, is crafted from cotton. It is denser and opaque compared to voile, making it a popular choice for lining designer garments.
Key Uses:
Batiste finds its application in various areas, with notable uses including:
- Shirting
- Tops
- Dresses
- Skirts
- Lingerie

Advantages
- Lightweight
- Soft
- Drapable
- Breathable
Disadvantages
- No Heat Retention
- Easily Wrinkled
Calico (Muslin)

Originating in India, calico is a simple, unbleached cotton fabric used historically for everyday textiles and clothing.
Key Uses:
Calico finds its application in various industries, including:
- Pattern making
- Toiles
- Aprons
- Quilts

Advantages
- Breathable
- affordable
Disadvantages
- Prone to shrinkage
- Less durable
Cambric (Batiste)

From France, cambric is a lightweight cotton or linen fabric valued for its smooth, lustrous finish and fine weave.
Key Uses:
Cambric finds its application in various industries, including:
- Handkerchiefs
- Fine linens
- Shirting

Advantages
- Breathable
- Soft
Disadvantages
- Can wrinkle easily
- Delicate
Canvas

Historically used for sails, canvas is a durable plain-weave fabric now popular in various robust applications.
Key Uses:
Canvas finds its application in various industries, including:
- Bags
- Shoes
- Workwear
- Upholstery

Advantages
- Strong
- Versatile
Disadvantages
- Can be stiff
- Heavy
Explore Our Canvas Fabrics
-
Per Metre Plain Cotton Canvas - 55" Wide (Pale Green)
Ab £600£900Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar -
Per Metre Plain Cotton Canvas - 55" Wide (Maroon)
Ab £600£900Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar -
Per Metre Plain Cotton Canvas - 55" Wide (Pink)
Ab £600£900Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar
Cashmere

Cashmere, with its roots in the Kashmir region, is renowned for its ultra-soft texture and insulating properties.
Key Uses:
Cashmere finds its application in various industries, including:
- Sweaters
- Scarves
- Hats
- Gloves

Advantages
- Soft
- Warm
Disadvantages
- Requires delicate care
- Expensive
Explore Our Cashmere Fabrics
-
3 Metres Printed Cashmere Effect Crepe Fabric- 45" Wide (Squares)
£699£1800Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar -
Per Metre Printed Cashmere Effect Crepe Fabric- 45" Wide (Bloom)
£599Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar -
Per Metre Printed Cashmere Effect Crepe Fabric- 45" Wide (Grey Paisley)
£599Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar
Chambray

Chambray, a denim-look alike, is a breathable cotton fabric that originated in Cambrai, France.
Key Uses:
Chambray finds its application in various industries, including:
- Shirts
- Dresses

Advantages
- Durable
- Soft
- Lightweight
Disadvantages
- Can wrinkle
- Limited stretch
Damask

Damask boasts elaborate patterns and is revered for its aesthetic appeal on jacquard looms, often featuring reversible looks.
Key Uses:
Damask finds its application in various industries, including:
- Upholstery
- Drapery
- Table Linens
- Clothing

Advantages
- Durable
- Intricate designs
- Reversible patterns
Disadvantages
- Can be expensive
- Requires careful cleaning
Deadstock

Deadstock refers to unused fabric left over from mills or garment production, offering an eco-friendly material choice.
Key Uses:
Deadstock finds its application in various industries, including:
- Clothing
- Accessories
- Home decor

Advantages
- Sustainable
- Cost-effective
- Unique
Disadvantages
- Limited quantities
- Unknown durability
Denim

Denim is characterized by its indigo-dyed warp threads and sturdy twill construction, a staple for casual wear.
Key Uses:
Denim finds its application in various industries, including:
- Jeans
- Jackets
- Skirts
- Overalls

Advantages
- Durable
- Versatile
- Ages well
Disadvantages
- Can be stiff initially
- Requires multiple washes
Explore Denim Fabric
-
Denim Delight Fabric Bundle (3 x 2 Metres)
£2000£3600Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar -
Per Metre Made For England Rayon Suiting 58" Wide - (Denim)
£600£1000Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar -
Per Metre Made For England Rayon Suiting 58" Wide - (Stonewashed Denim)
£600£1000Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar
Dupione Silk

Dupione is distinguished by its slubbed texture and sheen, a sought-after fabric for its elegant and crisp drape.
Key Uses:
Dupione finds its application in various industries, including:
- Bridal wear
- Evening gowns
- Draperies

Advantages
- Luxurious feel
- unique texture
Disadvantages
- Delicate
- Prone to wrinkles
- Costly
Egyptian Cotton

Grown in the fertile Nile delta, Egyptian cotton is renowned for fibers that create exceptionally soft and luxurious textiles, perfect for high-quality bedding and fashion.
Key Uses:
Egyptian Cotton finds its application in various industries, including:
- High-end bedding
- Fine garments
- Towels

Advantages
- Soft
- Strong
- Breathable
- Easy to Wash
Disadvantages
- Easily Wrinkles
Elastane

Elastane refers to unused fabric left over from mills or garment production, offering an eco-friendly material choice.
Key Uses:
Elastane finds its application in various industries, including:
- Sportswear
- Swimwear
- Undergarments

Advantages
- Flexible
- Cost-Effective
- Stretchy
- Durable
Disadvantages
- Less durable over time
- Can lose elasticity
- Sensitive to Heat and Bleach
Faux Fur

A fabric that is made to look and feel like real fur. The origin of faux fur dates back to 1910 when low-pile fabrics were made to give the appearance of fur. It wasn't until the 1950's that synthetic fibers were used to create furs that resembled animals such mink. Because of the activism of the 1960's, faux furs gained popularity in fashion and continue to today. (see faux suede, faux leather).
Key Uses:
Faux Fur finds its application in various industries, including:
- Outerwear
- Trim

Advantages
- Abrasion resistance
- Ethical
- Good Resilience
- Thermal Retention
- Hydrophilic
Disadvantages
- Can cause irritation
Explore Faux Fur Fabric
Faux Leather

Sometimes referred to as leatherette, it is a fabric that is made to look and feel like real leather. Mostly seen with a fabric base and a PVC coating over its face, it is used in both fashion and home applications.
Key Uses:
Faux Leather finds its application in various industries, including:
- Upholstery
- Fashion Applications
- Book Binding

Advantages
- Ethical
- Durability
Disadvantages
- Environmental Impact
- Heat Sensitivity
- Breathability
Explore Faux Leather Fabric
-
3 Metre Cotton Linen Backed PVC 55” Wide (Linen)
£1000Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar -
Heavy Soft Leatherette Jersey 55” Light Khaki
£1000£3000Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar -
Heavy Soft Leatherette Jersey 55” Yellow
£1000£3000Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar
Faux Suede

Artificial suede utilizes man-made fibers to achieve the nap and texture of natural suede, complete with a brushed, plush finish.
Key Uses:
Faux Suede finds its application in various industries, including:
- Apparel
- Decorative trim
- Interior design

Advantages
- Ethical
- Cost-Effective
- Easy to Maintain
- Durability
Disadvantages
- Breathability
- Environmental Impact
Felt

Felt, an ancient textile, is created through the process of matting, condensing, and pressing fibers together, bypassing the need for looms or spinning yarn. This fabric, often found in the traditional wear of nomadic Asian cultures, is primarily made from wool but can also include synthetic fibers.
Key Uses:
Felt finds its application in various industries, including:
- Cold-Weather Clothing
- Footwear
- Crafting

Advantages
- non-Fraying
- Insulating
- Compact
- Retains Shape
Disadvantages
- Prone to Pilling
- Absorbs Water
- Not Durable
Flannel

Flannel is a soft woven fabric, known for its warmth and comfort. It's typically made from wool, cotton, or a synthetic blend. The fabric's softness is achieved through a process called 'napping', where the fibers are brushed to create a raised texture. Flannel is often associated with cold-weather clothing due to its excellent heat retention.
Key Uses:
Flannel finds its application in various industries, including:
- Winter clothing
- Bedding
- Crafting

Advantages
- Warm
- Soft
- Breathable
- Versatile
Disadvantages
- Pilling
- Maintenance
- Shrinking
Hare

Rabbit or hare fur, popular since the 1920s, primarily adorns hats, trims, and coats. Known for its softness and density, this fur is versatile in length and easily dyed, enhancing its desirability in the fur industry.
Key Uses:
Hare finds its application in various industries, including:
- Hats
- Coats
- Trim

Advantages
- Soft Texture
- Dense
- Dye-Friendly
- Thermal Retention
Disadvantages
- Ethical Concerns
- Can Shed
- Requires Special Care
Harris Tweed

Protected by law, Harris Tweed is a hand-woven fabric from Scotland’s Outer Hebrides, made with local virgin wool. Its tradition-rich production results in warm, breathable, and high-quality tweed, varying in color and pattern.
Key Uses:
Harris Tweed finds its application in various industries, including:
- Home Decor
- Accessories
- Fashion

Advantages
- Warm
- Durability
- High-Quality
Disadvantages
- Requires Dry Cleaning
- Costly
Hemp

Dating back to 8,000 B.C., hemp is a linen-like fiber from the cannabis plant, historically used for making sails. Today, it's renowned for its strength, versatility, and eco-friendliness, used in everything from fabric to bioplastics.
Key Uses:
Hemp finds its application in various industries, including:
- Textiles
- Ropes
- Eco-Friendly
- Paint
- Plastics

Advantages
- Strong When Wet
- Non-Static
- Hydrophilic
- Resistant To Mold and Mildew
Disadvantages
- Poor Draping Qualities
- Flammable
- Lacks Flexibility
Jersey Knits

Originating from Jersey in the Channel Islands, jersey knit became popular for more than undergarments after Coco Chanel's pioneering use in the early 20th century. Known for its stretch and fluid drape, it’s a single knit fabric ideal for casual wear.
Key Uses:
Hare finds its application in various industries, including:
- T-Shirts
- Tops
- Dresses
- Skirts

Advantages
- Soft Texture
- Stretchy
- Comfortable
- Lightweight
- Wrinkle-Resistant
Disadvantages
- Prone to Unraveling
- Hem Curling
Jute

Jute, a shiny and soft vegetable fiber, is second to cotton in economic affordability. Historically used in British military uniforms, it now mainly serves in interior textiles. Known for its golden-brown hue and durability, jute is also eco-friendly but deteriorates quickly when exposed to moisture.
Key Uses:
Jute finds its application in various industries, including:
- Ropes
- Twines
- Mats
- Uniform Fabrics

Advantages
- Soft
- Durability
- Eco-Friendly
- Breathable
Disadvantages
- Rough Texture
- Moisture-Sensitive
Explore Jute Fabric
-
Per Metre Heavyweight Hessian Fabric – Premium Upholstery Grade (White)
£795£1299Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar -
10 Metre Hessian Fabric Bundle
£2500£7500Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar -
10 Metre Polyester Hessian Fabric Bundle
£2000£7500Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar
Kashmir

Originating from the Kashmir region and found in countries like India and China, the Kashmir goat produces the coveted cashmere fiber. Extracted from the underbelly, this fiber is celebrated for its exceptional softness and warmth, outperforming sheep’s wool in insulation. The natural shades of the fiber include white, black, brown, and gray, and it can be dyed various colors. However, due to the rarity of Kashmir goats, cashmere is a highly prized material.
Key Uses:
Kashmir finds its application in various industries, including:
- Sweaters
- Scarves
- Outerwear

Advantages
- Lightweight
- ultra-Soft
- Comfortable
- Highly Insulating
Disadvantages
- Requires dry cleaning
- Less Durable
Kenaf

Kenaf, known scientifically as hibiscus cannabinus, is a plant with fibers similar to jute, used historically in Egypt over 3,000 years ago. It's an eco-friendly alternative in textile production, given its rapid growth rate, low carbon footprint, and biodegradability, making it suitable for fabrics, ropes, and even bioplastics.
Key Uses:
kenaf finds its application in various industries, including:
- Ropes
- Twines
- Mats
- Uniform Fabrics

Advantages
- Sustainable
- Eco-Friendly
Disadvantages
- Rough Texture
Knit

Knit fabric, created from interlocking yarn loops, offers significant stretch, sometimes up to 500%. Available in various types like rib, double, cable, and jersey knits, it's made either by hand or machine. Knit fabrics, which date back to the first millennium AD, are categorized as either warp or weft knits, each offering unique characteristics.
Key Uses:
Knit finds its application in various industries, including:
- Sweaters
- Suits
- Outerwear

Advantages
- Stretchy
- Warm
Disadvantages
- Prone to snagging
Lace

Originating in the late 1400s, lace is an intricate openwork fabric created using various techniques like needle, bobbin, and crochet. Once exclusive to royalty due to its labor-intensive process, modern lace is popular in bridal and fashion, with varieties like Chantilly and Venise Lace.
Key Uses:
Lace finds its application in various industries, including:
- Bridal Attire
- Fashion
- Trims
- Home Décor

Advantages
- Delicate
- Elegantly
- Versatile
Disadvantages
- Requires Dry Cleaning
- Costly
- Less Durable
Explore Lace Fabric
-
3 Metres Luxurious Rachelle Lace- 55" Wide (Sale 12)
£500£1500Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar -
3 Metres Luxurious Rachelle Lace- 55" Wide (Peach)
£300£1500Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar -
Per Metre, Metallic Trimming, 45mm Wide (Black & Light Gold)
£300£500Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar
Lambs Wool

Harvested from lambs around seven months old, lamb's wool is valued for its supreme softness and elasticity. It's a high-quality, breathable fiber, ideal for both warm and cool weather garments.
Key Uses:
Lambs wool finds its application in various industries, including:
- Sweaters
- Scarves
- Hats

Advantages
- Extremely Soft
- Insulating
- Breathable
Disadvantages
- Requires Dry Cleaning
Latex

Latex, a type of natural rubber, is noted for its waterproof properties and flexibility. Initially used for rain gear, it's now popular for body-hugging clothing like leotards and gloves but can tear easily.
Key Uses:
Latex finds its application in various industries, including:
- Rainwear
- Leotards
- Bodysuits
- Gloves

Advantages
- Stretchy
- Waterproof
Disadvantages
- Prone to Tearing
Leather

Used since 5,000 B.C., leather, made from animal hides, is a versatile material utilized in various products. Renowned for its durability and adaptability to temperature changes, leather is a staple in fashion and upholstery.
Key Uses:
Linen finds its application in various industries, including:
- Clothing
- Home Textiles

Advantages
- Durable
- Breathable
- Non Static
Disadvantages
- Wrinkles Easily
- Flammable
- Less Flexible
Explore Leather Fabric
-
3 Metre Cotton Linen Backed PVC 55” Wide (Linen)
£1000Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar -
Heavy Soft Leatherette Jersey 55” Light Khaki
£1000£3000Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar -
Heavy Soft Leatherette Jersey 55” Yellow
£1000£3000Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar
Lycra

Developed during WWII, Lycra, a variation of spandex, offers exceptional elasticity and has become a staple in activewear and swimwear.
Key Uses:
Lyrcra finds its application in various industries, including:
- Sportswear
- Swimwear
- Fashion Clothing
- Undergarments

Advantages
- Highly Elastic
Disadvantages
- Wears Over Time
- Sensitive To Heat
Explore Lycra Fabric
-
3 Meters Lycra Crepe Jersey 55" Wide (High Street 36)
£500£3000Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar -
3 Meters Dressmaking Lycra Jersey 55" Wide (Men)
£999£3000Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar -
3 Metres Super Soft Printed Lycra Jersey 55" Wide (Jingle)
£650£1500Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar
Madras

Originating from Madras, India, Madras is a lightweight, often plaid-patterned cotton fabric used historically in head wraps in the Middle East and Africa. Made with fragile, short-staple yarns that give it a unique texture, this fabric is known for its color change with each wash due to non-fast dyes.
Key Uses:
Madras finds its application in various industries, including:
- Shirts
- Shorts
- Pajamas
- Blazers
- Trousers

Advantages
- Breathable
- Textured Feel
Disadvantages
- Colours Can fade
Mesh

Mesh is a fabric characterized by its open, hole-filled weave, offering a range of applications from athletic wear to fashion.
Key Uses:
Mesh finds its application in various industries, including:
- Lingerie
- Sportswear
- Shapewear
- Costumes

Advantages
- Stretchable
- Lightweight
- Breathable
Disadvantages
- Not Durable
Muslin

Muslin, a plainly woven cotton fabric, varies from being a test fabric for patternmaking in the U.S. to a lightweight, sheer textile in other regions. It’s versatile for various applications, including clothing and fittings.
Key Uses:
Muslin finds its application in various industries, including:
- Garments
- Tops
- Dresses

Advantages
- Breathable
Disadvantages
- Flammable
Explore Muslin Fabric
-
16 Farben verfügbar
Soft Cotton Muslin - 44" Wide - 16 Variations Available
£250Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar -
Muslin Fabric Bundle- 10 Metres (Bright Colours)
£2500£4000Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar -
Muslin Fabric Bundle- 10 Metres (Essential Colours)
£2500£4000Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar
Neoprene

Developed by polymerizing chloroprene, Neoprene is known for its use in scuba gear, where rubber is encased in polyester. It's valued for maintaining flexibility across temperature ranges and chemical stability. Modern neoprene, often used in fashion, substitutes rubber with air cushioning, resulting in scuba knits.
Key Uses:
Neoprene finds its application in various industries, including:
- Wetsuits

Advantages
- Water-Resistant
- Heat-Retentive
- Durable
- Flexible
Disadvantages
- Limited Breathability
Nylon

Nylon, a robust and lightweight synthetic polymer, is known for its exceptional strength, elasticity, and resistance to abrasion and chemicals. It's used in a variety of products, from clothing to outdoor gear, thanks to its quick-drying properties and resistance to insects and weather elements.
Key Uses:
Nylon finds its application in various industries, including:
- Parachutes
- Tents
- Outdoor Clothing
- Fishing Gear

Advantages
Durable
Lightweight
Quick Drying
Disadvantages
- colour fades in sunlight
Organic Cotton

Grown without genetic modification or pesticides, organic cotton is a more sustainable and eco-friendly option for textiles. It's commonly used in various garments and home decor, offering a softer feel compared to conventional cotton, with reduced exposure to toxins.
Key Uses:
Organic Cotton finds its application in various industries, including:
- Shirts
- Trousers
- Loungewear
- Home Textiles

Advantages
- Soft
- Eco-Friendly Cultivation
Disadvantages
- Prone To Wrinkling
- More Expensive
Organic Linen

Derived from flax plants cultivated without pesticides or synthetic fertilizers, organic linen is an environmentally friendly textile. It's used in a range of clothing items and offers benefits due to the lack of processing toxins.
Key Uses:
Organic linen finds its application in various industries, including:
- Shirts
- Suits
- Skirts
- Trousers

Advantages
- Strong
- Lightweight
- Breathable
- Toxin Free
Disadvantages
- More Costly Than Conventional Linen
- Wrinkles Easy
Ottoman

Characterised by its pronounced crosswise ribs larger than those in faille or bengaline, Ottoman is a stiff fabric that resists gathering or shirring. It's ideal for structured garments and upholstery but should not be fitted too tightly to avoid seam slipping and cracking.
Key Uses:
Ottoman fabric finds its application in various industries, including:
- Formal Wear
- Dresses
- Upholstery

Advantages
- Easy To Clean
- Soft
Disadvantages
- Not a Versatile Fabric
Oxford Cloth

A basket-woven fabric often used in dress shirts, Oxford cloth combines two fine warp yarns with a heavier, softly-spun fill yarn for a distinctive look. Available in pure cotton or rayon blends, it's known for its durability and breathability.
Key Uses:
Oxford cloth fabric finds its application in various industries, including:
- Casual Dresses
- Shirts

Advantages
- Durable
- Breathable
Disadvantages
- Requires Frequent Cleaning
Polyester

A synthetic fiber derived from polyethylene terephthalate, polyester gained fame in the 1970s for its use in leisure and clubwear. Today, it's widely used in various apparel, costuming, and as a filler material due to its unique properties. This versatile material is also utilized in performance fabrics, home furnishings, and technical applications like insulation and water-resistant coatings.
Key Uses:
Polyester finds its application in various industries, including:
- Upholstery
- Sleeping bag
- Costumes

Advantages
- Wrinkle Resistance
- Retains Shape
- Retains Heat
Disadvantages
- Not Eco-Friendly
- Static
- Heat Sensitive
Explore Polyester Fabric
-
3 Metres Bundle Embroidery Crepe- 45" Wide (Sale 126)
£500£3000Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar -
3 Metres Bundle Embroidery Crepe- 45" Wide (Sale 125)
£500£3000Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar -
3 Metres Bundle Embroidery Crepe- 45" Wide (Sale 124)
£500£3000Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar
PVC

PVC, a widely used thermoplastic polymer, often features a polyester fiber backing with a shiny plastic coating, known as vinyl in the U.S. It's recognized for its durability and versatility, commonly seen in various products from upholstery to footwear.
Key Uses:
PVC linen finds its application in various industries, including:
- Handbags
- Upholstery
- Rainwear
- Shoes
- Vinyl Products

Advantages
- Durable
- Cost-Effective
- Versatile
Disadvantages
- Not Eco-Friendly
- Heat Sensitive
Satin

Satin, known for its glossy surface and smooth texture, is a weave that typically features a lustrous front and a matte back. This fabric is produced using filament fibers such as silk, nylon, or polyester, woven in a manner that creates a shiny, smooth surface. Satin's luxurious appearance makes it popular for formal wear, lingerie, and bedding. Its weave allows light to reflect off the surface, giving it a characteristic sheen.
Key Uses:
Satin finds its application in various industries, including:vening gowns and formal attire
- Evening gowns and formal attire
- Lingerie and sleepwear
- Bedding and linens
- Interior decoration items like curtains and cushion covers
- Accessories like ties and scarves

Advantages
- Silky Texture
- Comfortable
Disadvantages
- Prone To Snagging
- Not Very Breathable
- Slippery
Sheeting Fabrics
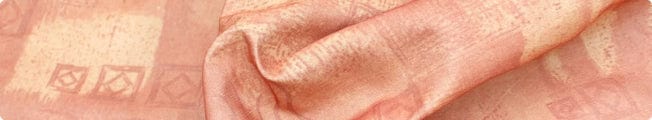
Sheeting fabric is a broad category of tightly woven fabrics, typically made from cotton or cotton blends, known for their durability and smooth finish. It's commonly used in the production of bed linens due to its comfort and strength. This fabric comes in various thread counts, with higher counts indicating a finer weave and softer texture. Sheeting is designed to withstand frequent washing and usage, making it a practical choice for household linens.
Key Uses:
Sheeting fabrics linen finds its application in various industries, including:
- Bed sheets and pillowcases
- Summer clothing
- Quilts
- Drapery Linings
- Table Linens

Advantages
- Durable
- Durable
- Soft
- Breathable
Disadvantages
- Expensive
- Does Not Retain Heat
- Wrinkles Easily
Explore Our Sheeting Fabrics
-
Luxury Poly Cotton Blend Sheeting 90" (Sheeting 21)
Ab £600Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar -
Luxury Poly Cotton Blend Sheeting 90" (Sheeting 20)
Ab £600Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar -
Luxury Poly Cotton Blend Sheeting 90" (Sheeting 19)
Ab £600Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar
Taffeta

Taffeta is a crisp, smooth woven fabric known for its lustrous sheen and distinctive rustle. Traditionally made from silk, modern variations also include synthetic fibers like nylon and polyester. Taffeta is woven tightly, resulting in a fine, durable fabric with a slightly stiff texture. It's particularly famous for its use in elegant evening wear and formal garments, where its structure allows for voluminous silhouettes.
Key Uses:
Taffeta finds its application in various industries, including:
- Evening gowns and ball dresses
- Lingerie and Sleepwear
- Wedding and Bridal Attire
- Lining
- Curtains

Advantages
- Holds its Shape
- Durable
- Versatile
Disadvantages
- High Maintenance
- Rustles
- Wrinkles Easily
Explore Our Taffeta Fabrics
-
3 Metre Premium Taffeta Lining 55" (Sale 87)
£500Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar -
3 Metre Premium Taffeta Lining 55" (Sale 86)
£500Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar -
3 Metre Premium Taffeta Lining 55" (Sale 85)
£500Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar
Tapestry

Tapestry fabrics are rich, intricately woven textiles featuring complex designs or scenes, almost like artwork. Historically used as wall hangings for insulation and decoration in castles, tapestries are woven on a loom and often include various colors and textures of thread to create detailed images or patterns. Modern tapestry fabrics are used in a variety of decorative applications, blending art and function. They are typically made from materials like cotton, wool, or synthetic fibers, giving them a substantial and durable quality.
Key Uses:
Tapestry fabrics finds its application in various industries, including:
- Wall Hangings
- Upholstery
- Hangbags
- Rugs

Advantages
- Versatile
- Durable
Disadvantages
- Heavy
- Careful Cleaning
Explore Tapestry Fabric
Tartan

Tartan is a patterned fabric consisting of criss-crossed horizontal and vertical bands in multiple colours. Originally made from woven wool, tartans are now also produced in other materials. It's most famously associated with Scottish heritage, each pattern or "sett" traditionally representing a Scottish clan. Tartans are not limited to clothing but extend to various fashion and home décor items. The patterns are created by weaving differently colored threads to form distinctive checks.
Key Uses:
Tartan finds its application in various industries, including:
- Kilts
- Jackets
- Home Decor
- Upholstery

Advantages
- Historical Significance
- Versatile
- Durable
Disadvantages
- Expensive
- High Maintenance
Explore Our Tartan Fabrics
-
3 Metre Premium Cotton Drill 55" Wide (Tartan 6)
£1500£3000Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar -
3 Metre Premium Cotton Drill 55" Wide (Tartan 5)
£1500£3000Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar -
3 Metre Premium Cotton Drill 55" Wide (Tartan 4)
£1500£3000Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar
Terry Fabric

Terry fabric, often referred to as terry cloth, is a woven fabric known for its looped pile on one or both sides. This looping technique provides excellent absorbency, making it a popular choice for towels and bathrobes. Typically made from cotton, terry fabric can also include blends of polyester or linen. The loops increase the surface area, allowing the fabric to absorb large amounts of water. Terry cloth varies in weight and thickness, offering different levels of absorbency and comfort.
Key Uses:
Terry fabrics finds its application in various industries, including:
- Towels
- Baby Accessories
- Beachwear
- Sportswear

Advantages
- Absorbent
- Comfortable
- Durable
- Soft
Disadvantages
- Heavy
- Prone to Shrinkings
Explore Our Terry Fabrics
-
Cotton Looped Backed Terry Jersey 74" Wide (Black)
Ab £799£1500Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar -
Cotton Looped Backed Terry Jersey 74" Wide (Blue)
Ab £799£1500Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar -
Cotton Looped Backed Terry Jersey 55" Wide (Mint)
Ab £799£1500Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar
Towelling

Terry fabric, often referred to as terry cloth, is a woven fabric known for its looped pile on one or both sides. This looping technique provides excellent absorbency, making it a popular choice for towels and bathrobes. Typically made from cotton, terry fabric can also include blends of polyester or linen. The loops increase the surface area, allowing the fabric to absorb large amounts of water. Terry cloth varies in weight and thickness, offering different levels of absorbency and comfort.
Key Uses:
Towelling fabrics finds its application in various industries, including:
- Towels
- Baby Accessories
- Beachwear
- Sportswear

Advantages
- Absorbent
- Comfortable
- Durable
- Soft
Disadvantages
- Heavy
- Prone to Shrinkings
Velvet
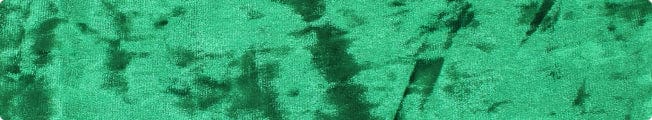
Velvet is a sumptuous fabric characterized by its dense pile of evenly cut fibers that give it a distinctive soft feel. This luxurious texture is achieved by weaving two thicknesses of the material simultaneously, then cutting them apart, creating the pile effect. Traditionally made from silk, modern velvet is often produced using cotton, rayon, or synthetic fibers, making it more accessible. Velvet is renowned for its opulence and depth of color, lending itself well to both fashion and home décor.
Key Uses:
Velvet fabrics finds its application in various industries, including:
- Formal Wear
- Upholstery
- Cushions
- Bags
- shoes

Advantages
- Luxurious
- Durable
Disadvantages
- Heavy
- High Maintenance
Explore Our Velvet Fabrics
-
3 Metres Printed Spandex Velvet- 55" (Sale 78)
£500£3000Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar -
3 Metres Velvet Look Furnishing 60" Wide (Purple)
£699£3000Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar -
3 Metres Versatile Striped Light Velvet 60" Wide (Grey)
£899£3000Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar
Wool

Wool, a natural fiber obtained from sheep and other animals, is renowned for its warmth and durability. It's made from the soft, curly hair of these animals and is spun into yarn, which is then woven or knitted. Wool's crimped fibers create tiny air pockets, making it naturally insulating. It's a versatile fabric used in a range of clothing, from casual to formal wear, as well as in home furnishings. Wool can absorb moisture without feeling wet, adding to its comfort in various climates.
Key Uses:
Wool fabrics finds its application in various industries, including:
- Sweaters, Cardigans & Jumpers
- Blazers
- Suits
- Blankets & Throws
- Scarves, Hats & Gloves

Advantages
- Warm
- Durable
- Flame resistant
- Environmentally Friendly
Disadvantages
- Prone to Shrinking
- High Maintenance
Explore Our Wool Fabrics
-
3 Metres Premium Wool Rich Fabric 55" Wide (Green & White)
£1500£3000Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar -
3 Metres Premium Wool Rich Fabric 55" Wide (Black, White & Gold)
£1500£3000Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar -
3 Metres Premium Wool Rich Fabric 55" Wide (Zebra)
£1500£3000Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar
Upholstery Fabric

Upholstery fabric is a durable and sturdy material specifically designed for covering furniture. It's crafted to withstand significant wear and tear, maintaining its shape and appearance over prolonged use. These fabrics come in various materials, including natural fibers like cotton and wool, synthetic fibers like polyester and nylon, and blends. Upholstery fabrics are available in a wide range of colors, patterns, and textures, allowing for customization and design flexibility in interior decorating. They are often treated for stain resistance and durability, making them ideal for furniture that sees regular use.
Key Uses:
Upholstery fabrics finds its application in various industries, including:
- Furniture
- Vehicle Interior
- Decor

Advantages
- Durable
- Variety
Disadvantages
- Expensive
- High Maintenance
Explore Our Upholstery Fabrics
-
3 Metres Luxury Plain Chiffon- 55" Wide - (Sale 79)
£500£2400Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar -
3 Metres Luxury Plain Chiffon- 55" Wide - (Sale 40)
£500£2400Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar -
3 Metres Luxury Plain Chiffon- 55" Wide - (Sale 23)
£500£2400Grundpreis /Nicht verfügbar

 Fabric Catalogue
Fabric Catalogue




















































































































































